DFANet
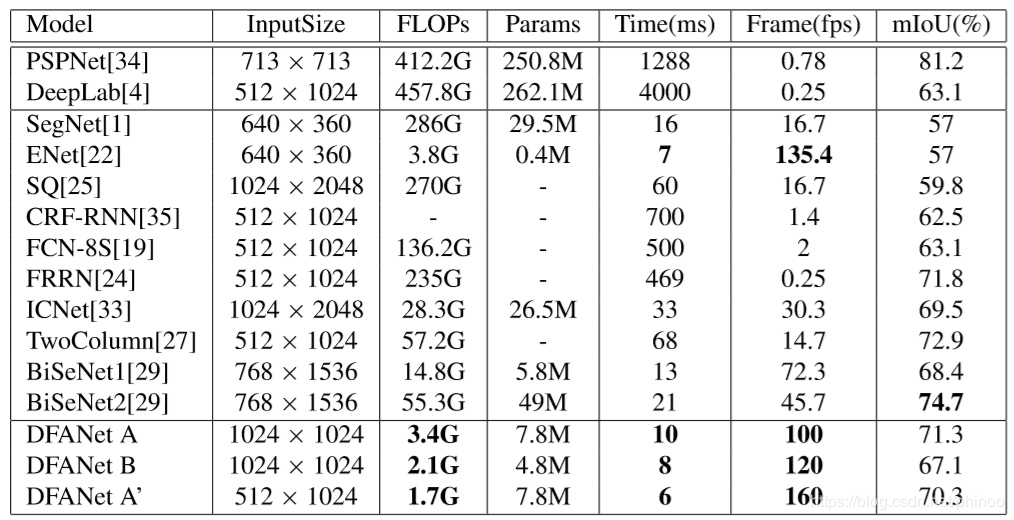
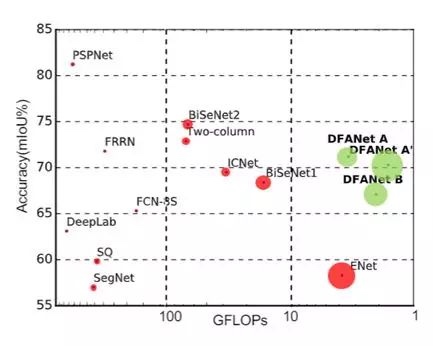
测试DFANet语义分割网络,基于论文DFANet: Deep Feature Aggregation for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation,主要特点在于它的实时性:
测试使用cityscapes数据集,可以在这里下载。
服务器及数据准备
假设有已有一个远程docker服务器root@0.0.0.0 -p 9999。
Dependence
1 | pytorch==1.0.0 |
1 | apt install -y libsm6 libxext6 |
检查pytorch版本:
1 | import torch |
1 | # Linux, pip, Python 3.6, CUDA 9 |
使用scp指令将本地程序和数据集上传到服务器:
1 | scp -P 9999 local_file root@0.0.0.0:remote_directory |
解压缩zip文件
1 | apt-get update |
下载DFANet
1 | git clone https://github.com/huaifeng1993/DFANet.git |
Pretrained model
打开utils/preprocess_data.py,修改dataset位置:
1 | cityscapes_data_path = "/home/luohanjie/Documents/SLAM/data/cityscapes" |
运行脚本,生成labels:
1 | python3 utils/preprocess_data.py |
main.py
打开main.py,修改dataset位置:
1 | train_dataset = DatasetTrain(cityscapes_data_path="/home/luohanjie/Documents/SLAM/data/cityscapes", |
2019.4.24 An function has been writed to load the pretrained model which was trained on imagenet-1k.The project of training the backbone can be Downloaded from here -https://github.com/huaifeng1993/ILSVRC2012. Limited to my computing resources(only have one RTX2080),I trained the backbone on ILSVRC2012 with only 22 epochs.But it have a great impact on the results.
由于我们没有ILSVRC2012的pretrained model,所以需要关掉标志位:
1 | net = dfanet(pretrained=False, num_classes=20) |
ERROR: TypeError: init() got an unexpected keyword argument 'log_dir'
打开train.py,修改为:
1 | writer = SummaryWriter(logdir=self.log_dir) |
ERROR: Unexpected bus error encountered in worker. This might be caused by insufficient shared memory (shm)
出现这个错误的情况是,在服务器上的docker中运行训练代码时,batch size设置得过大,shared memory不够(因为docker限制了shm).解决方法是,将Dataloader的num_workers设置为01。
打开main.py,修改:
1 | train_loader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, |
Train
1 | python3 main.py |
https://blog.csdn.net/hyk_1996/article/details/80824747↩︎